Cystic Fibrosis: Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung injury / infection model
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common pathogenic bacteria found in the lungs of cystic fibrosis sufferers, P. aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen and promotes accelerated decline of pulmonary function. Due to its ability to produce alginate and form biofilms it is difficult to treat with standard antibiotics.
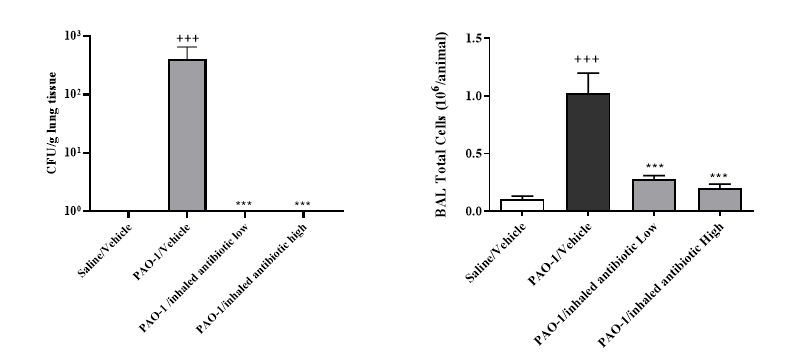
We have two models, a lung injury acute model which induces an inflammatory response but bacteria is cleared by 72 hours as well as a chronic model where bacteria are embedded in agarose beads, high titres of P. aeruginosa in both models cause an acute lethal infection.
| Study Design | |
|---|---|
| Species/Strain | C57BL/6J mouse |
| Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung injury / infection model |
| Relevant Use | Efficacy of novel antibiotics and antibacterials |
| Readouts Available | Daily Bodyweights and Clinical Signs, Bacterial load, BAL differential cell counts, BAL cytokines and Pathology (H&E and PAS) |
Study data generated by Labcorp Huntingdon Pharmacology.
Related Models
-
Bhas 42 Cell Transformation Assay (CTA)
Carcinogenicity, Discovery, Toxicology -
Monocrotaline induced Pulmonary Hypertension (PAH)
Discovery -
Asthma: Ovalbumin sensitization and challenge
Discovery -
Chlorine Induced Lung Injury
Discovery -
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) neutropenic thigh infection model
Discovery -
COPD: LPS + fMLP PK/PD model – Neutrophil Elastase Targets
Discovery -
COPD: Human Neutrophil Elastase Lung Hemorrhage Model
Discovery -
Bronchoconstriction models for LABA, LAMA & MABAs
Discovery
